Understanding A Motorcycle Electrical System and Components on your Motorcycle!
The motorcycle electrical system and components sound and appear very complicated. The mass of wires found on a motorcycle can be confusing if not marked neatly during the build.
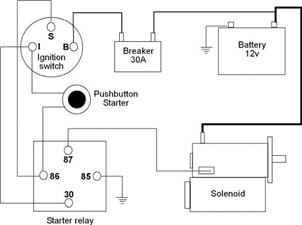
What comprises a motorcycle wiring and electrical system? The electronic components may differ somewhat from motorcycle to motorcycle based on what options are included which require electric power. However, there are basic components that are common to all motorcycles.
Wiring Harness: The 'wiring harness;, a large bundle of wires routed inconspicuously fro point to point sometimes traveling inside the tubular frame, provides the key to the electric system of any. The wires are passed from the power source e(battery or generator) to all the various components of the overall electrical system.
Battery: The battery is the heart of the motorcycle electrical system. It stores 12 volt power and allows it to be used on-demand. Battery cables transfer the power from the battery to the electrical harness and components.
Fuse Block, Fuses: In order to prevent power surges from destroying parts of the electrical system, there is a small fuse block which contains fuses controlling specific portions of the electrical system.
Spark Plugs and Wires or Electronic Fuel Injectors (EFI): Spark plugs create a spark to ignite the fuel in each cylinder using the power passed to them from the spark plug wires. In the case of a motorcycle with EFI, electricity is still required to ignite the fuel to generate power by moving the pistons and values.
Head Lights, Tail Lights, Other "Running Lights": Electric power is delivered through the wiring harness to the lead and tail lights to provide power to light these devices. Some motorcycles, especially 'dressers', have other running lights which require electric power as well.
Alternator, Generator, Regulator, Relay: The alternator, also called the generator, recharges the battery when the motorcycle has the engine cranked. The regulator ensures that the electric power passing to or from the battery through the wiring harness is within the proper voltage range to prevent damage to parts.
Electric Start System: Motorcycles can be started by turning the engine over using the kick starter. However, this process can be a lot of work and a bit precarious since the motorcycle must be balanced while one foot is brought up to the kick starter and a lot of pressure must be applied very quickly to turn over a high compression engine. It requires a very strong person to do this. To solve this dilemma, electric starters allow the engine to be cranked with the press of a button.
This is not an exhaustive explanation of the electrical system or electrical components on your motorcycle. It is only intended to give you an overview of the major items and how they work together to allow you a safe, comfortable ride.